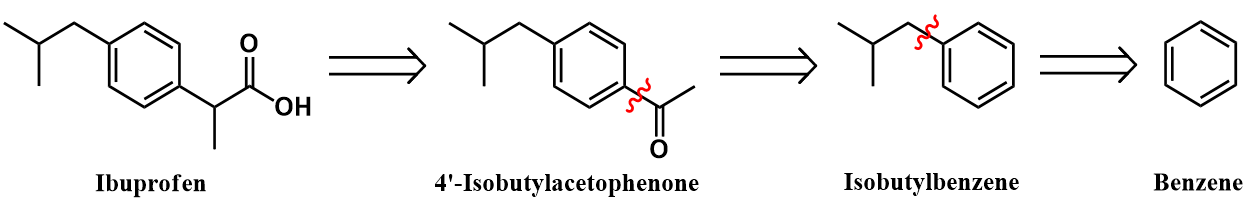
Retrosynthetic analysis
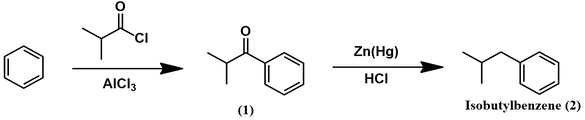
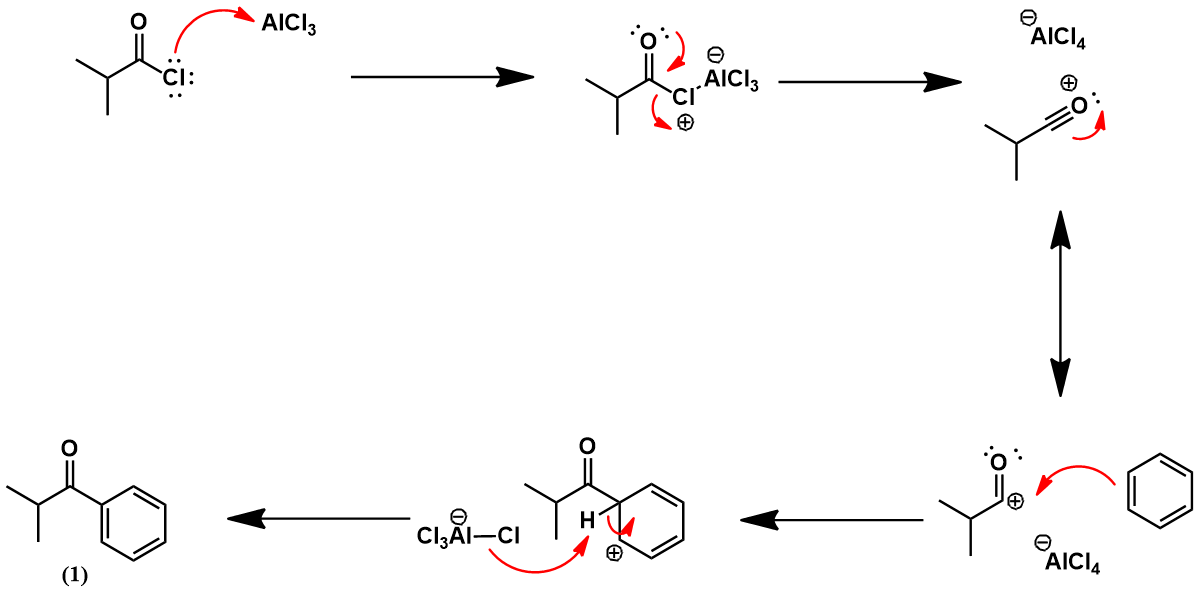
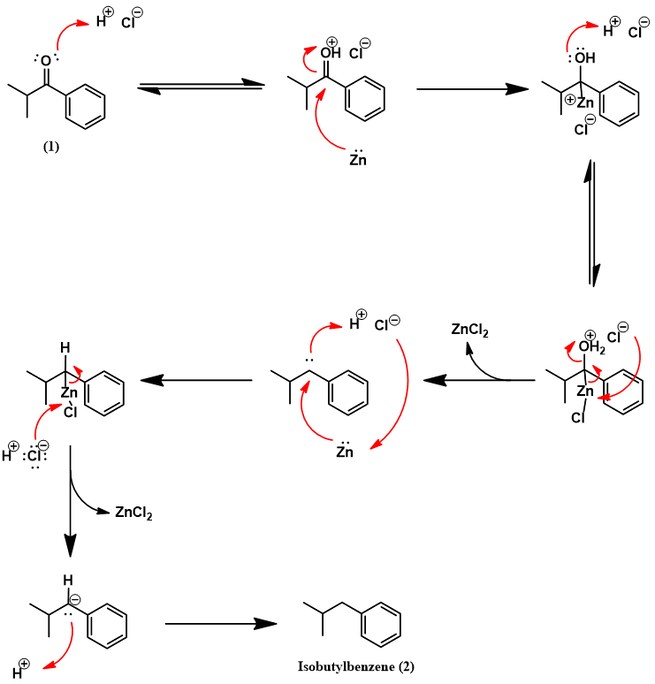
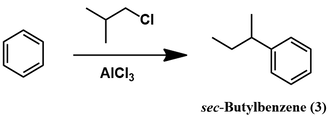
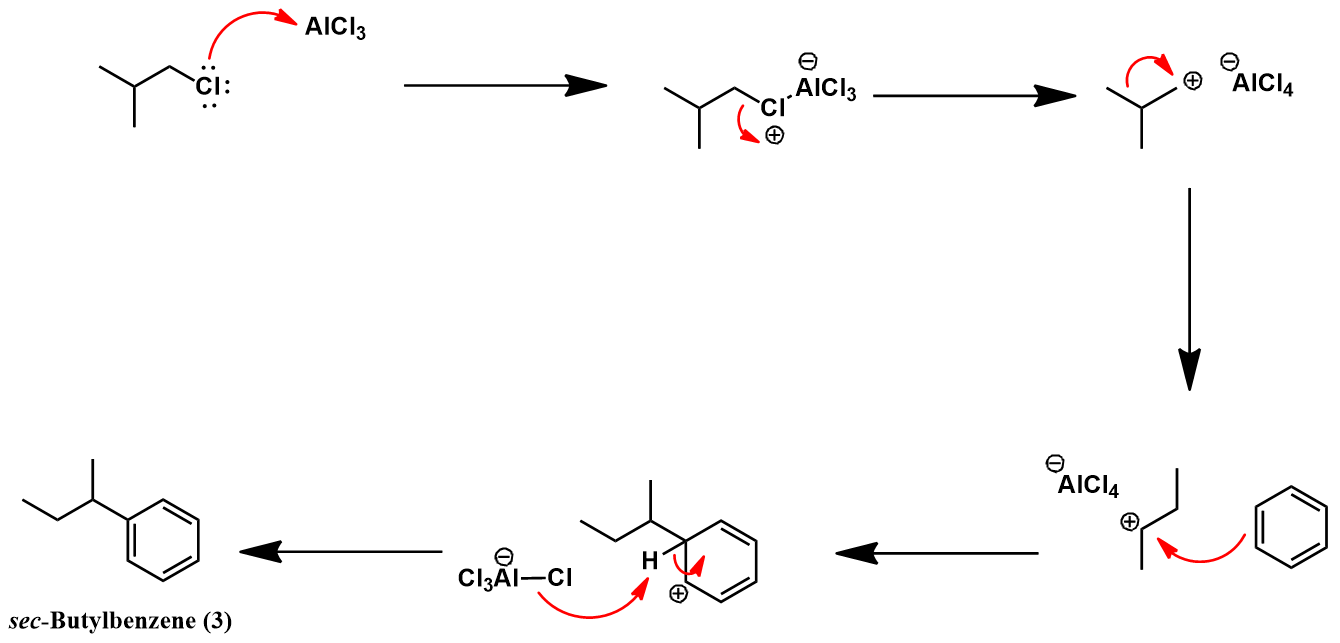
Synthesis of isobutylbenzene from benzene
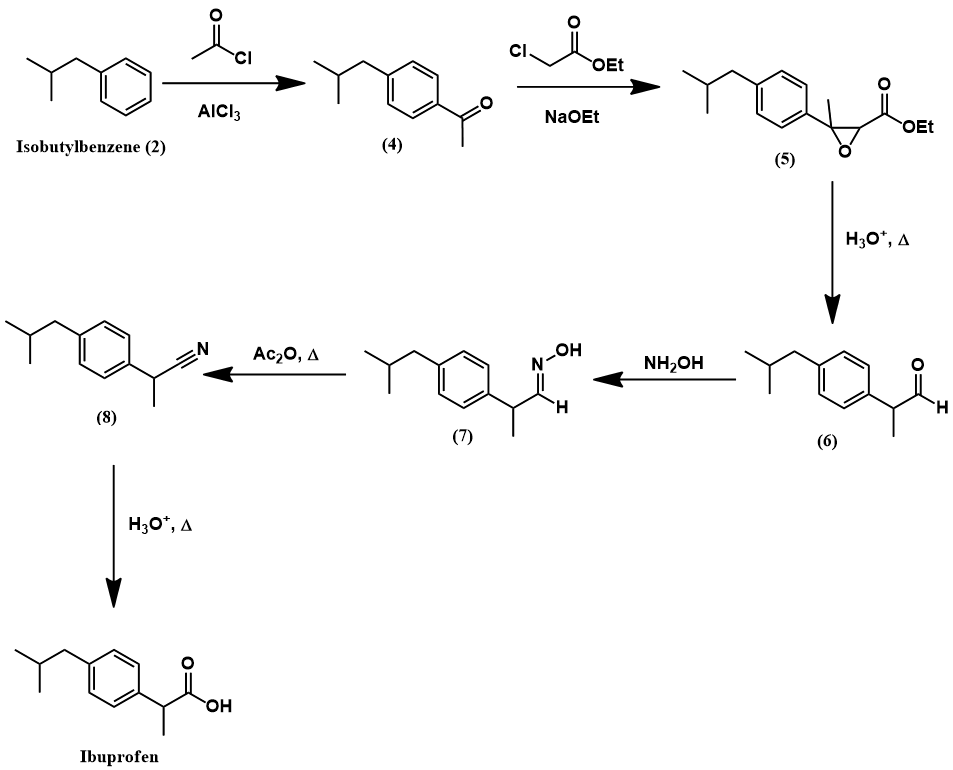
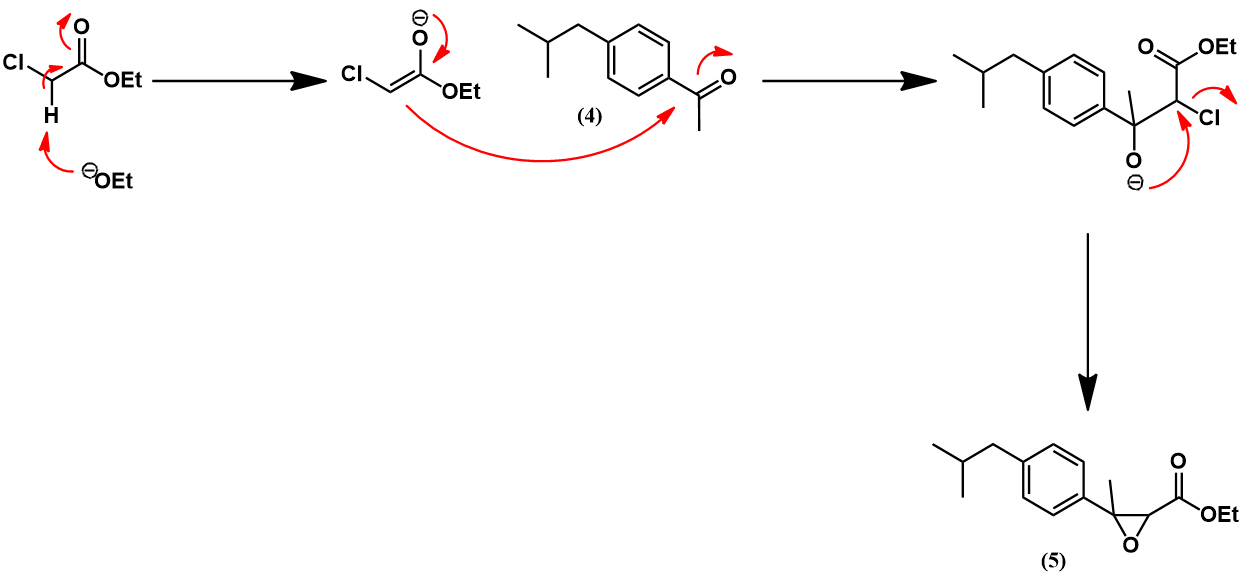
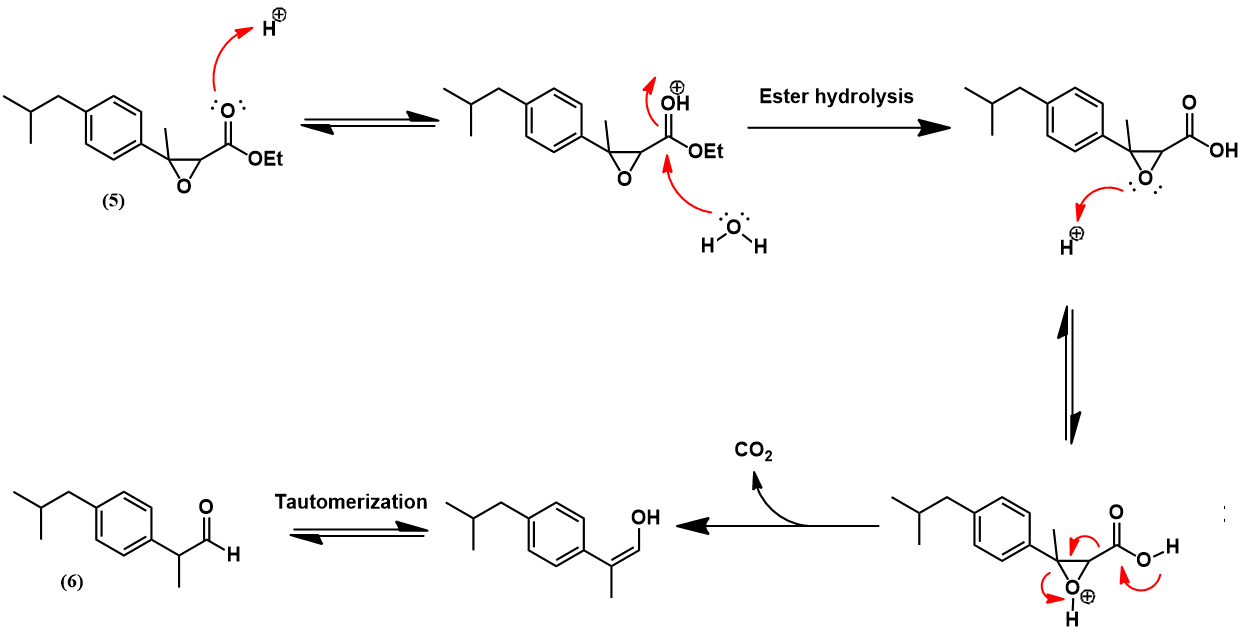
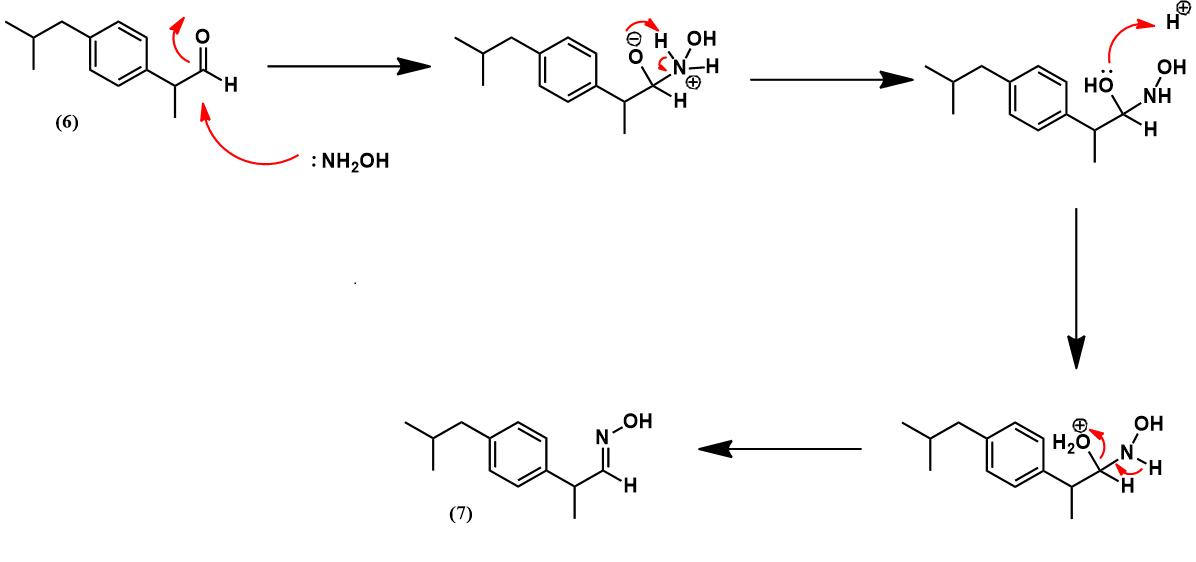
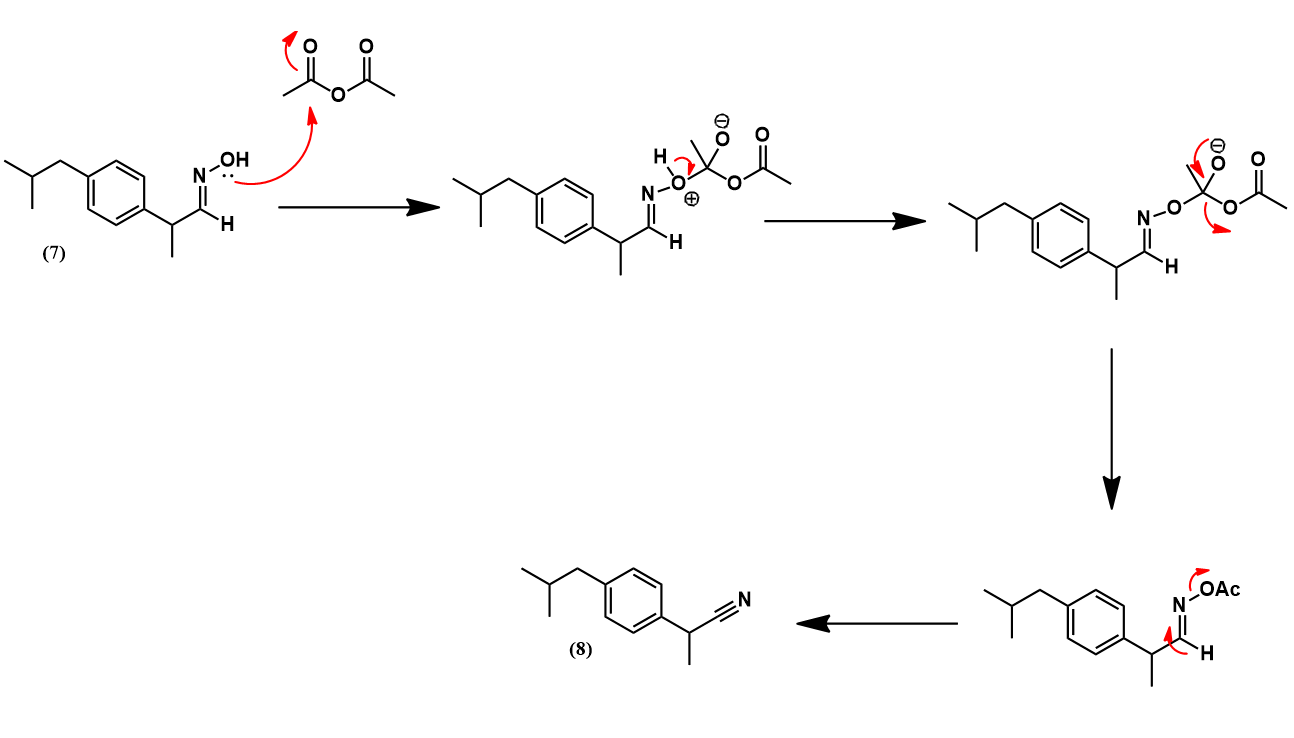
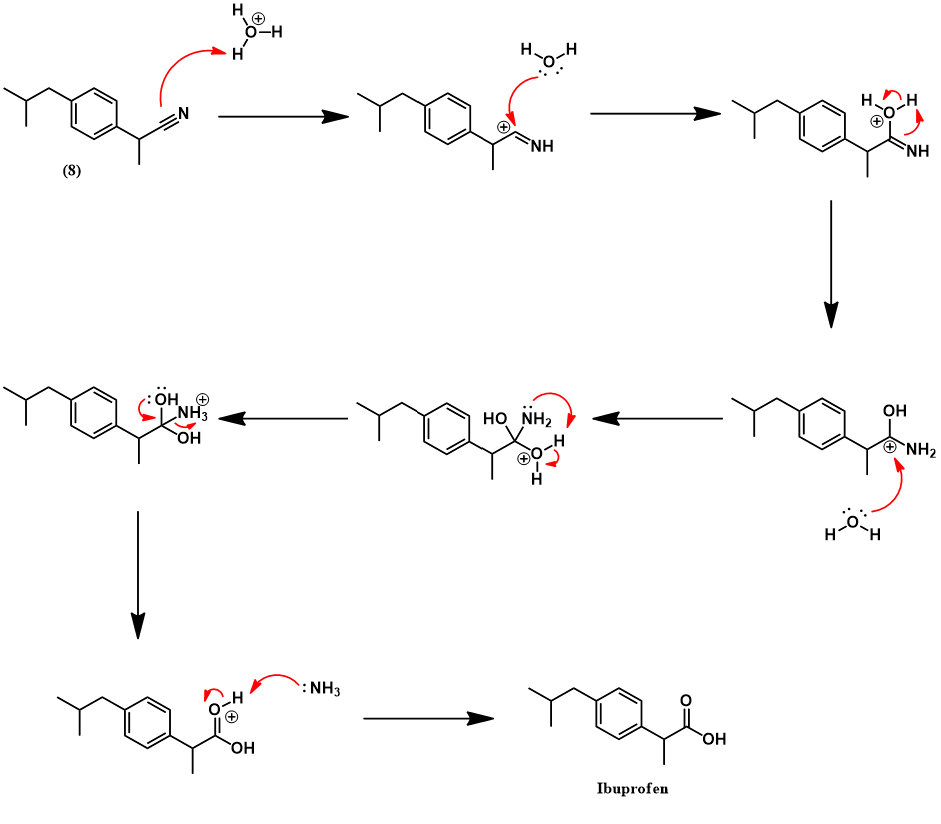
Synthesis of ibuprofen by the Boots process [2]
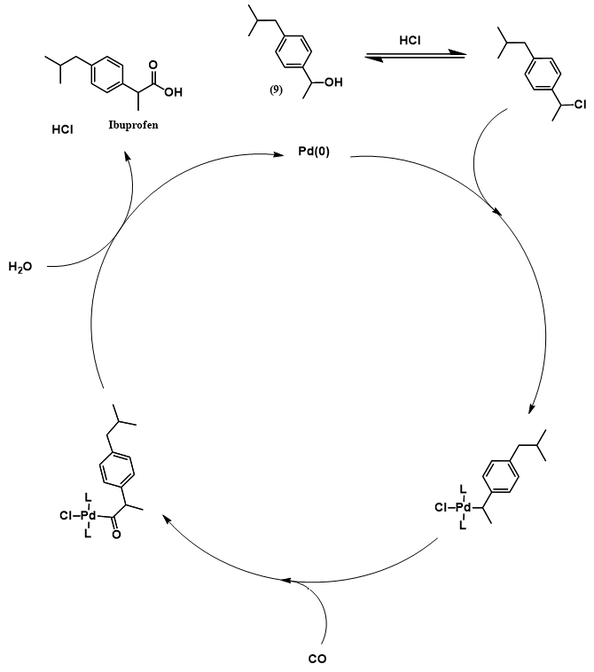
The Boots-Hoechst-Celanese ibuprofen synthesis [3]
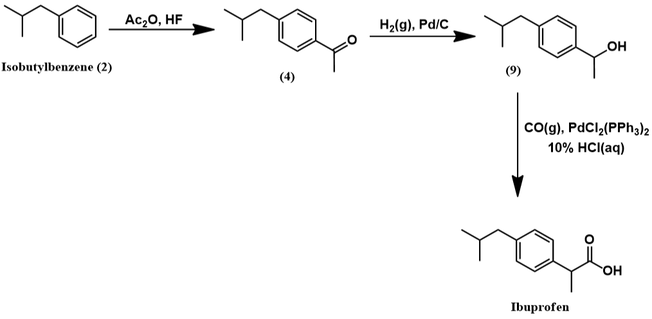
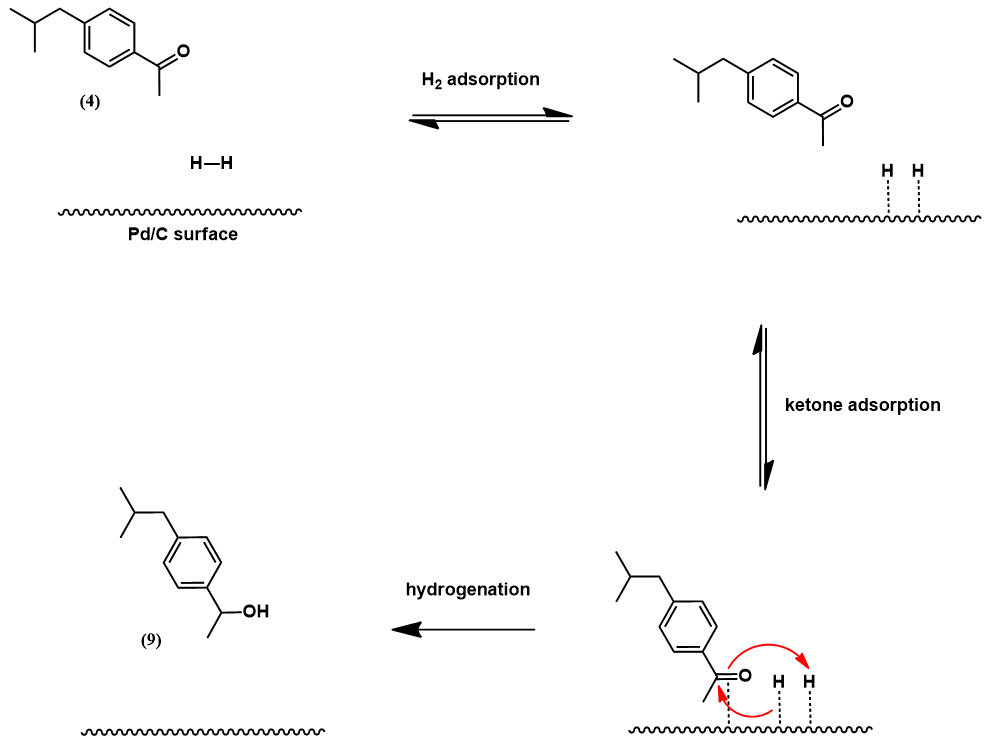
Mechanistically, the Friedel-Crafts acylation of isobutylbenzene to (4) proceeds in identical fashion as shown earlier for the Boots process. However, HF replaces the Lewis acid catalyst and acetic anhydride replaces acetyl chloride. The next synthetic step is a pallidum-catalyzed hydrogenation of aromatic ketone (4) to alcohol (9). The palladium catalyst facilitates the reaction through activation of H2 by surface adsorption. The ketone also adsorbs to the palladium surface [5]. This brings it in proximity to the activated H2 and promotes hydrogenation. These steps are represented schematically below.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed