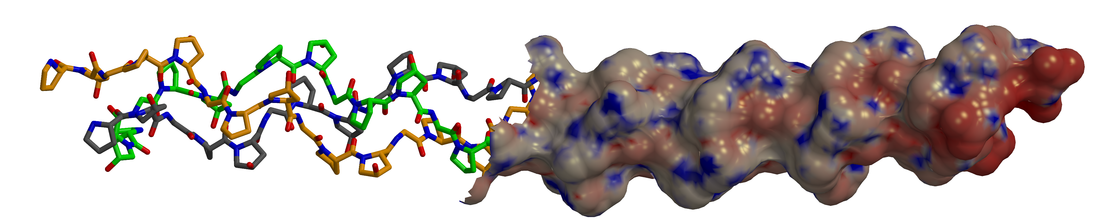
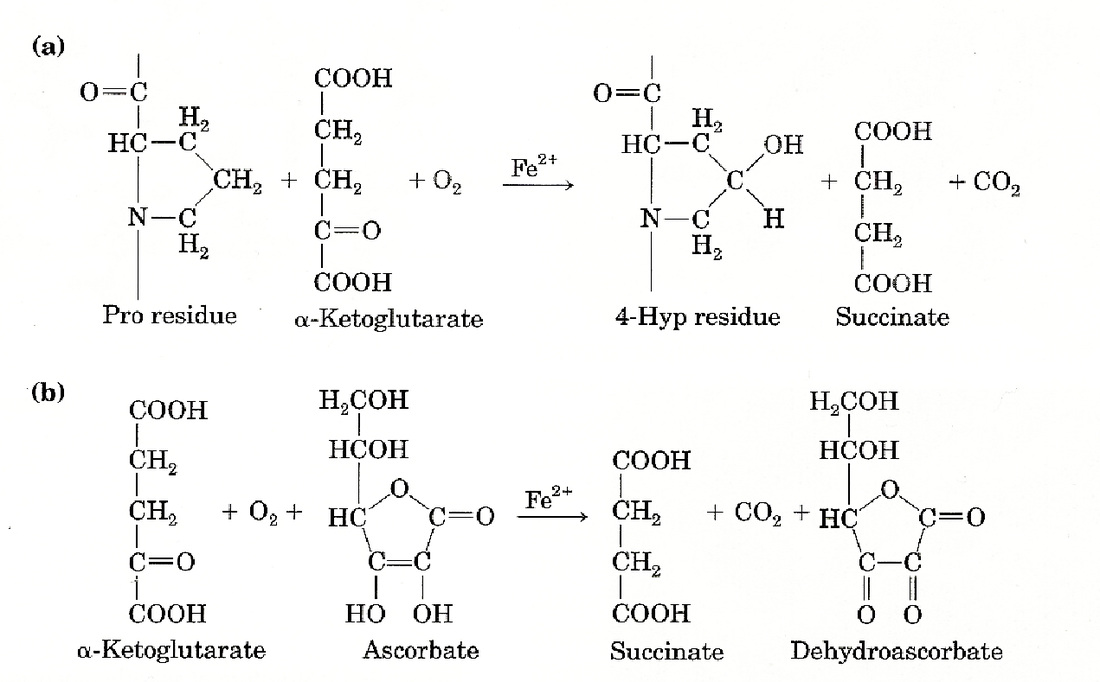
Vitamin C must be important in collagen biosynthesis because a deficiency in it results in a defective form of the protein. The triple helix is looser and less strongly cross-linked, greatly reducing its tensile strength. This leads to the particularly unpleasant condition called scurvy. In order to understand how vitamin C is essential, we must examine the process by which collagen is made. First, a related protein called procollagen, the precursor to collagen, is synthesized. It must then undergo several types of posttranslational modifications to create collagen. Vitamin C is relevant to the hydroxylation of proline residues in the Y positions. This modification is necessary to produce functional collagen (I will explain why this is later). The hydroxylation is done by an iron-containing enzyme called prolyl 4-hydroxylase. Oxygen, the proline residue, and another molecule called α-ketoglutarate interact with the enzyme. The proline residue is hydroxylated while the α-ketoglutarate undergoes oxidative decorbaxylation, making succinate and carbon dioxide. “A” in the figure below shows the reaction. The role of vitamin C is not in this reaction, but rather an unrelated reaction which prolyl 4-hydroxylase happens to also catalyze. As before, oxidative decorbaxylation of α-ketoglutarate occurs. However, in this reaction the enzyme’s iron becomes oxidized, rendering the enzyme inactive. Vitamin C (called ascorbate in the figure) reduces the enzyme’s iron, restoring it to its active state. “B” in the figure shows the overall process. This therefore is the mechanism by which vitamin C deficiency causes the production of defective collagen. A lack of active prolyl 4-hydroxylase results in a failure to hydroxylate Y position proline residues on procollagen.
With scurvy ultimately being caused by a lack of hydroxylation of proline residues, you may be wondering what is so special and important about hydroxyproline. Luckily the issue has been widely studied. It was long thought that the hydroxyl groups facilitated hydrogen bonding through a large network of water molecules which stabilized the triple helix [2]. There was X-ray crystallography data which supported this model where extensive hydration and water-mediated intramolecular hydrogen bonding occurred. However, it was later discovered that for some triple helices (such as proline-hydroxyproline-glycine) replacing the hydroxylproline with proline did not change the extent of hydration. Furthermore, hydroxyproline’s stabilizing effect has even been observed under anhydrous conditions. The hypothesis that water-facilitated hydrogen bonding is responsible for the increased stability therefore had to be discarded.
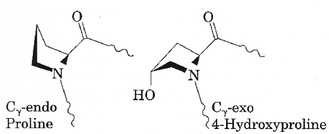
Another notable feature of the hydroxyl group is its high electronegativity, it withdraws electrons. Hence it was suggested that this could be the important characteristic. A collagen analogue where the hydroxyl group on the hydroxyproline was replaced with fluorine was developed. Fluorine is also very electronegative, but does not contribute appreciably to hydrogen bonding. Not only did these polypeptides spontaneously assemble into triple helices, but the helices were even more stable than normal collagen. This would be expected if electron-withdrawing effects were the key factor, fluorine is more electronegative. It turns out that the electron withdrawal affects which conformation proline tends to be in. Proline can exist in one of two conformations, Cγ-exo and Cγ-endo. Both are shown in the following diagram.
In order for collagen to achieve the proper folding, the proline residues in the Y positions must be in the Cγ-exo conformation, while the proline residues in the X positions need to be in the Cγ-endo conformation. The electron-withdrawing hydroxyl, if at the right location on the molecule, causes proline to favour the Cγ-exo conformation. This accounts for why hydroxylation must be done on the Y position proline residues only.
In summary, eat lots of fresh fruit and vegetables rich in vitamin C. Nobody wants unhydroxylated Y position proline residues in their collagen molecules!
References:
[1] Cox MM, Nelson DL. 2008. Principles of biochemistry. 5th ed. New York: W. H. Freeman and Company, p. 124-8.
[2] Gorres KL. 2009. Substrate recognition by prolyl 4-hydroxylase [dissertation]. [Madison (WI)]: University of Wisconsin-Madison.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed